Salmastra Nedir ?
As it is known, the shaft seal is one of the main elements of centrifugal pumps. It is mandatory to use it in all centrifugal pumps except pumps with magnetic coupling (without seal). In this article, we will try to share with you the types and working mechanics of the seal.
The main function of the seal in a centrifugal pump is to provide sealing between the wet and dry areas in the pump. The wet zone is the side of the pump body where the fluid is pressurized and mechanical energy is converted into hydraulic energy. The dry zone is the shaft, bearings and engine side outside the wet zone.
In order to better understand the function and working principle of the seal, it is useful to briefly touch upon the working logic of the centrifugal pump.

First of all, the motor located in the dry zone takes energy from the network, converts electrical energy into mechanical energy and carries this energy to the pump shaft through the coupling. One end of the shaft is connected to the coupling side, that is, the dry area, and the other end is connected to the fan in the pump body, which we call the wet area. In this way, the shaft rotates the fan inside the body. The fan converts mechanical energy into hydraulic energy by pressurizing the fluid thanks to its blades.
When we look at this working mechanics, the main problem with sealing is that one part of the shaft is in the dry part and the other part is in the wet area (creating an opening in the pump body), and at the same time, the shaft is a moving, that is, rotating element. We can produce two different solutions to prevent fluid leakage from the body to the outside. The first solution is to drive the pump fan with a different method, not with a shaft connected to the motor. In this case, it would be appropriate to use a pump with a magnetic coupling. Another solution would be to use an additional element that will both allow the shaft to rotate and minimize leakage from the pump body. We call this element the packing.
The most commonly used seal types today are mechanical and soft seals. Although both types have their own advantages and disadvantages, as the quality of industrial production increases, the usage rate of mechanical seals also increases. The reason for this situation will become clear a little later when we explain how both seals work.
Yumuşak Salmastra

Soft packing can be defined as a piece of equipment that provides sealing by physically filling the gap between the shaft and the body, which we just mentioned above. Soft packings are wrapped on the shaft in different numbers of rows "or on a bushing placed on the shaft to protect the shaft from wear". In this way, both sealing is ensured and the rotation of the shaft is allowed. However, it should not be forgotten that soft packings never provide complete sealing, and it is even desirable not to provide them. Because of the constantly occurring friction force, the seals heat up and their surface friction increases. For this reason, there must be constant fluid on the seal, so that the seal can cool and the friction will be reduced, at least partially. Although the amount of this leakage is theoretically stated as 1-2 drops per minute, field observations have shown that this number is 5 to 10 drops per minute even in the best systems. This leakage amount is adjusted by the seal pressure element on the pump.
Mekanik Salmastra
Mechanical seals are used for exactly the same purpose, but their working system is quite different. Mechanical seals consist of two parts. These; They are fixed and movable elements. The fixed element is mounted on the pump and does not move. The movable element is mounted on the shaft or on a bushing that rests on the shaft and rotates simultaneously with the shaft.
The working system of the mechanical seal is as follows; While the fluid passes through the pump, the fixed element on the body side (in the high pressure region) is pushed towards the moving element on the motor side due to the fluid pressure. A spring on the movable side allows this movement and supports the movable seal surface. Thus, the surfaces of the movable and fixed elements almost adhere to each other. However, since one side is constantly rotating and the other side is constantly fixed, if these surfaces are completely stuck to each other, the surfaces will wear out and break due to friction in a short time and the seal will no longer be able to function. For this reason, a very small gap is formed between the fixed and moving element surfaces. This gap is approximately 0.0008mm long. The fluid pumped in the pump fills the resulting gap and forms a very thin film layer between the two surfaces.
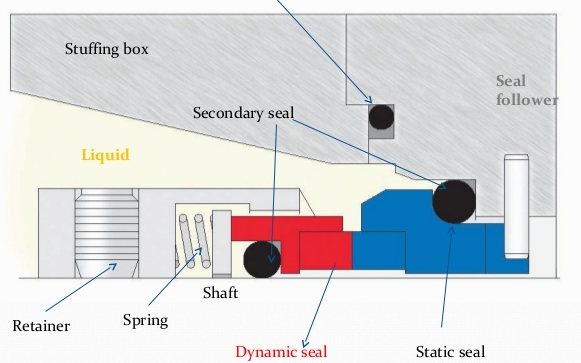
Since there are many articles, videos and animations about the working principle of mechanical seals, we have briefly summarized the subject. If you would like to examine the working logic in detail or ask questions, you can contact us.
Yumuşak Salmastra mı Mekanik Salmastra mı?
Both seal types have their own advantages and disadvantages. The issue that should be taken into consideration when choosing a seal is the needs of the system and the facility. For example, if an expensive fluid is being transferred, it would be appropriate to use a mechanical seal to reduce the sealing to zero. Likewise, if the pumped fluid poses a risk to humans and the environment, and therefore zero leakage is desired, mechanical seals are the best choice. However, in an environment where the loads on the pump are high or where there are frequent small-scale movements on the ground where the pump sits, the soft packing will be more appropriate to use as it can tolerate axial misalignment much better.
| Mekanik Salmastra | Yumuşak Salmastra | |
| Advantages (+) |
||
| Provides Nearly 100% Sealing | Price advantage | |
| Doesn't Require Much Maintenance | Ease of Assembly | |
| Long Working Life | High Axial Misalignment Tolerance | |
| Disadvantage (-) |
||
| Prices are High | Requires Much Maintenance | |
| It is More Difficult to Install. | Cannot Provide 100% Sealing | |
| Axial Misalignment Tolerance is Very Low. | Damages Shaft or Bushing in a Short Time | |
The pros and cons of mechanical and soft seal types are briefly summarized above. However, it should not be forgotten that pump manufacturers will make the best choice regarding this issue. Because the type of seal is a material that must be selected by taking into account the fluid, the system in which the pump is located, and the structure of the pump itself. At the same time, pump manufacturers are likely familiar with the site and environmental conditions to be selected and have pumps operating in these systems. Therefore, they will recommend the most suitable shaft seal based on experience.


